 NA-MIC Project Weeks
NA-MIC Project Weeks
Back to Projects List
AR in Slicer
Key Investigators
- Alicia Pose Díez de la Lastra (Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Madrid, Spain)
- Javier Pascau (Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Madrid, Spain)
- Csaba Pinter (Ebatinca S.L., Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain)
- Lucas Gandel (Kitware, France)
- Adam Rankin (Robarts Research Institute / Western University, Canada)
- Jean-Christophe Fillion-Robin (Kitware, USA)
- Mónica García-Sevilla (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria , Gran Canaria , Spain)
- Houssem Gueziri
Project Description
Augmented Reality has increase its adoption in many areas with exciting benefits. Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (Madrid, Spain) has already worked in several medical projects based on AR (see their progress in https://biig-igt.uc3m.es/augmented-reality/). On these studies, they usually export information from Slicer to an alternative software (Unity).
The ultimate goal of this project is to check if it is possible to incorporate this technology directly to 3D Slicer in order to centralize the working process, at the time of benefiting from all Slicer tools.
Objective
- Learn what can be done in AR using 3D Slicer.
- Explore possible paths to integrate AR in 3D Slicer in the future.
- Study if we can receive transformations in Unity from Slicer, so that we can transfer navigation information between the two softwares.
Some links of interest:
- Writing a Holographic Remoting remote app using the OpenXR API
- Slicer Documentation on Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality support
Approach and Plan
- Develop a new Slicer extension called SlicerAR that streams AR directly to HoloLens 2.
Progress and Next Steps
- AR Support (OpenXR) in VTK:
The WIP branch supporting Holographic remoting to stream VTK rendering inside the Hololens has been submitted here. The immediate actions to take are listed there in the TODOS section: 1. and 2. should be addressed to reuse this work in SlicerVR.
-
Alicia and Lucas tried to replicate in Alicia’s computer the steps of the WIP branch Lucas’ shared above. They summarized them in this pdf document. Despite they were not able to complete the final step, they found out and fixed many new issues that improved the project.
-
Alicia, Houssem and Étienne Léger also met to discuss some features related to pattern recognition in HoloLens with Vuforia and ArUco, latency and interconnectivity between Slicer and Unity.
-
Alicia and Naghmeh additionally talked about connecting 3D Slicer and Unity in real time to send transformations between them. Here, here and here you can find two GitHub projects that explain how to achieve this connection via OpenIGTLink.
-
Alicia and Étienne met again after Project Week to discuss further about Étienne’s work. He tracks a tool connected to Plus and Slicer via OpenIGTLink. He managed to send this information, in real-time, to a self-developed AR tablet application (MARIN) using IBIS. Everything is programmed in Qt (check out the Qt creator from Qt.io to start programming in Qt).
Illustrations
Here below you can find some AR implementations in health by Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (Madrid, Spain) in the past years:
HoloLens 2 in Orthopedic Oncological Surgeries:
![]()
Smartphone app to communicate with the patient and help him/her understand his/her condition:

Real-time guidance during Open Cranial Vault Remodeling using smartphone:
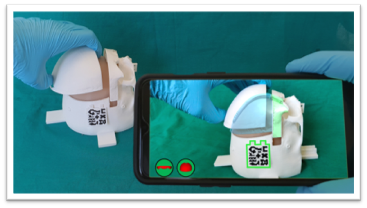
Needle Insertion Guidance for Sacral Nerve Stimulation using smartphone:
